

This is where we must intervene and override the default copy constructor. The data member (pointer) of the second object would then point to a memory location which no longer exists because we have already deleted the first object. Now, imagine what happens if we try to release the memory of one object. What we want is two identical but distinct objects but what we get is a dynamic member (pointer) in two separate objects pointing to the same memory location. This is definitely not what we want and is trouble uncalled for. As a result, data pointers from two distinct object points to the same memory location when standard copy constructor is invoked. This means that it would copy the pointer content, which is an address to a location, and not the values contained in the address. A typically standard copy constructor may be sufficient, but in some cases, a simple copying of values is not exactly what we want, especially when the object contains dynamic members (pointers). What it does is simply copy data members of the object passed to it to the corresponding data members of the new object. This is called a default or standard copy constructor. Then, what the compiler does is that it creates a minimal version of the same. Suppose a class does not have an explicit copy constructor. Sometimes, it does exactly what we do not want, especially with dynamic initialization. But, we must be very careful in relying on the default copy constructor. Note that, if we do not provide any explicit copy constructor, the C++ compiler provides a default one.
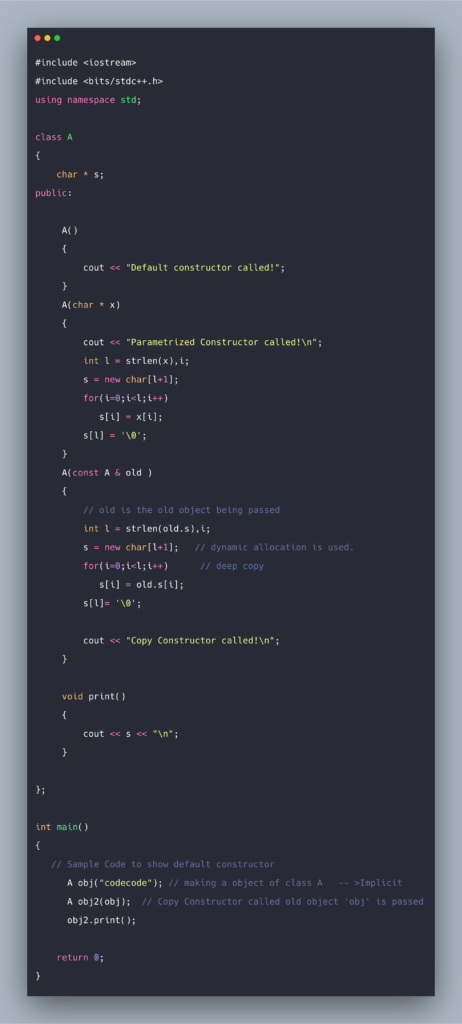
This is the reason why argument of the copy constructor is by reference and not by value. The argument by reference, on the other hand, is not a copy therefore, there is no question of invoking the copy constructor. As a result, the copy constructor would itself invoke the copy constructor recursively.


But, note that, as we define an explicit constructor in a class, the C++ compiler stops providing a default constructor. Default constructors are no-argument constructors therefore, if we want to send any argument in the constructor, we must do so with an explicit definition. The constructor call is implicit and, if we explicitly do not create a constructor, the C++ compiler provides one for us, called the default constructor. This ensures that objects are created and data members are initialized appropriately before being used. And, constructors usually are declared as public.Ĭ++ relies on the constructor call to create an object. Unlike member functions, another distinctive feature is that a constructor never returns a value, not even void. This naming scheme makes it distinct from the other member functions of the class. Initialization is done with the help of a constructor, a special member function defined as the same name as the class name. This is important because using an object with uninitialized data members makes these members prone to unintended problems. What Are Constructors?Īccording to the Object Oriented Programming principle, when an object of a class is instantiated, its data members should be initialized properly during creation. This article gets into some of the conceptual details about copy constructor with appropriate examples in C++. It also helps in control passing and returning of user-defined types by value during function calls. There are many intricate details about how it operates and how it is used. As the name suggests, a copy constructor is typically used to create a copy of an object.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
